Patrick J McCullough, Douglas S Lehrer, and Jeffrey Amend
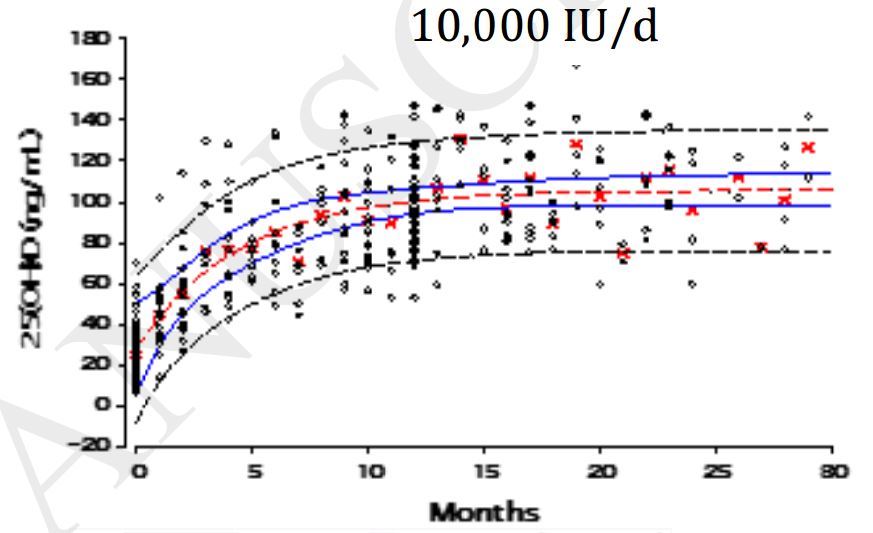
Deficiency of vitamin D is incredibly common due to a lack of sun exposure and absence of it in food sources, and the link between deficiency and increased risk for a variety of diseases is high. In the past, vitamin D has been reported to improve some diseases significantly by adequate exposure of sunlight to the skin, or oral or topical supplementation with vitamin D. These diseases include psoriasis, asthma, rickets, rheumatoid arthritis, and tuberculosis. The patients, 4,700, volunteered to supplementation with either 5,000 or 10,000 IUs a day. Those with increased disease concerns, volunteered for larger amounts, ranging from 20,000 to 50,000 IUs a day. There were several results reported: no cases of adverse events of vitamin D3 induced hypercalcemia were found; three patients with psoriasis showed significant clinical improvement supplementing 20,000 to 50,000 IUs a day; 418 patients on D3 long-term developed normal vitamin D blood levels. In conclusion, the supplementation of vitamin D3 ranging from 5,000 to 50,000 IU’s appears to be effective and safe.